Category
Why Us?
- Biggest SK-CZ vendor (since @2015) ako-tazit-kryptomeny.sk Now expanding to whole EU
- From this EU shop-version, you can even purchase directly from our wholesalers
- Contracted with 29 different wholesalers so always absolutely The lowest possible price of ASIC miners in EU
- Up 2 Year Warranty (instead of standard 6 months) to Bitmain miners
- Personal support to you with miners choice, profit calculations, recommendations ..
- Miner Setup for FREE
What is Cryptocurrency Mining and How it Works?
How does Bitcoin Mining work and What is it?
What is Bitcoin mining and How does it work is a quite common question, so we will explain it as for dummies. What is the principle of Bitcoin Mining and how this whole process takes place step-by-step? You will find out:
- From basic terms such as Blockchain, Block, Algorithm, Hashrate or Difficulty
- Throughth the explaining exactly what all those mining machines do?
- How mining works (step-by-step)?
- Why will be the Last Bitcoin in the world mined in 2141?
- Why do mining profits fall by exactly 50% (from day to day) once a 4 years?
- Who pays miners?
- Why would cryptocurrencies crash without miners?
PS: You may also be interested:
Is it Bitcoin Mining Still Worth? How Much do I Earn?

Cryptocurrency Mining – What Is It?
Cryptocurrency mining is a very specific activity where mining machines (miners) literally “produce” new cryptocurrency coins.
Think of mining as a cipher that you have to decipher. The more powerful your computer (miner) is, the faster it decodes and the faster you get a reward in the form of mined coins.
The whole principle is also described in the document called White Paper, which is perhaps the most important document of any digital currency.
All this mining process runs in a pre-planned schedule, when the exact amount of coins is mined in a certain time. And that is the whole principle of mining and its limitation (scarcity).
Exactly 328,500 Bitcoin coins are mined each year, regardless of whether the cryptocurrency is mined by 1 or 10 million miners worldwide.
The whole mining process works using the power of high-end computers, which solve thousands of complex mathematical operations in the network. But what does mathematical operations mean and what even that miners do? Read on ..
Anyway, nowadays, there are already 5 different ways to obtain mining power and thus ways how to mine Bitcoin, Ethereum, Zcash, Monero or other coins..
We have been covering all these 5 ways since 2015.
- Sale of specialized ASIC miners
- Manufacturing of Flexible GPU rigs
- New ECO HDD mining computers
- Cloud Mining – Hashpower rent
- Provide Hosting to gain cheap electricity in our 2 Mining Farms
The most popular and most profitable miners are ASIC and GPU. But which one pays off the most? Here are the 8 key differences between them, that significantly affect your profits.
How Does Crypto-Mining Work? (Step-by-step for Dummies)
How does bitcoin mining work step-by-step? What are all those miners actually doing? This is the most simple mining explanation. Read carefully.
Mining actually involves 2 chronological steps:
- Verification of transactions from the network
- At the same time, generating new coins of the cryptocurrency
All this takes the form of thousands of mathematical calculations performed by mining machines.
1. Transaction Verification
If you want to send 1,000€ throughth the bank to your friend, who will confirm and verify your transaction? Bank itself (center). The bank decides whether to approve or reject your transaction. And who does this controling in cryptocurrency network? Well, just cryptocurrency miners. Thousands of miners (dcentralized)!
If you want to send e.g. 1 Bitcoin to a friend, miners (computers) chceck:
- If you even have that 1 bitcoin (unauthorized spending)
- Whether the transaction is secure
- Whether there are not duplicated transactions (one transaction sent twice – double spending)
Miners verify if you really own the coins, if the transactions is secured ..
Only thanks to the miners, no one of theese mistakes can happen.
And right because of your 1 transaction is not verified by only 1 miner (center), but by thousands of miners around the world, cryptocurrencies are decentralized (unlike the bank, where the whole process is performed by 1 center). That´s first step of how bitcoin mining works.
2. Production of New Coins
There are 2 rewards for this miner´s activity:
- Transaction Fees (you send Bitcoin to someone, you pay a small fee for this transaction and this fee is the reward for the miners)
- The second reward for mining investors is the production of new block (coins) of cryptocurrencies. Thanks to that, new coins are gradually emited into the market (currently 6.25 BTC coins every 10 minutes).
And this is whole and clear explanation to: What is cryptocurrency mining all about and how it works.
Why are Miners So Important to Cryptocurrencies?
#Thanks to the miners, the entire network is 100% verified and 100% secure. The infallibility and accuracy of the data are guaranteed.
#Miners ensure the infallibility and unstackability of cryptocurrencies. There is no way to change or delete just 1 data from a blockchain database (database is stored in millions of miner hadwares around the world).
#Transactions are thanks to millions of miners confirmed and sent in a few minutes or even seconds (in bank you have to wait 1 or a several days).
#Fees are significantly lower, sometimes almost zero.
#Thanks to the miners, new cryptocurrency coins are emited to the market
Most Profitable Miners
Showing 1–4 of 11 results
Mining Terms
If you want to understand how whole mining works (in more detailed way) you have to understand this key terms and principles of mining.
#1 Blockchain (Technology and Chain of Block)
#1 Blockchain is the technology on which every single cryptocurrency in the world is built on. Technology that ensures the accuracy, infallibility, 100% security and non-falsification of cryptocurrencies.
All this thanks to “control” resp. verification of crypto-transactions. Transactions, as we explained above, are verified by millions of miners worldwide (unlike in banks, where this process is performed by 1 central system, making it so much more prone to errors or “manipulation” in favor of a certain result, which may not be objective).
#2 Blockchain is also a public “accounting book” (distributed ledger), which records every single sent transactions (from all over the world). But firstly, it have to be verified by miners before being written to the blockchain.
It stores transactions since the origin of the cryptocurrencies itself. Thus, in this “Blockchain database“ you can really look at the very first transaction made by Bitcoin from the 3. january 2009). Blockckahin is divided into smaller parts – blocks.
Whole database of transactions (Blockchain) is divided into smaller parts called blocks.
And theese single transactions are stored in mentioned database (Blockchain).
PS: More about blockchain technology and its use (Forbes article).
#2 Block in Blockchain
1 Block is therefore 1 small part of the Blockchain database, which contains information about all Bitcoin transactions around the world for exactly the last 10 minutes. Why in a period of ten minutes? Find out below.
- In any case, after 10 minutes, a new block is created and it is arranged chronologically after the last (previous) mined block, thus creates a chain of blocks (Blockchain).
PS: On the official Blockchain website, you can find an overview of all mined blocks with the exact block IDs, date and time, how long does it takes (always about 10 minutes), the count of contained transactions …
1 block = 10 minutes = 50 BTC coins
An important parameter is the block size and his period of mining. Each 1 block in the case of mother of cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin), originally in 2009 contained 50 BTC coins and they was mined exactly every 10 minutes (600 seconds). But .. :
- The number of Bitcoin coins is limited. Only 21 million BTCs that will be ever exist in the world.
- 1 block of Bitcoin in 10 minutes that is 144 blocks in 1 day
- 144 block * 50 BTC coins are 7200 mined BTCs daily (21 million coins in 8 years)
So would that mean that The last Bitcoin in the World will be mined after 8 years of existence? So in 2017? So it already was mined?
However, it is 2021 and Bitcoins are still mined today
- How is it possible? All thanks to the thing called Halving!
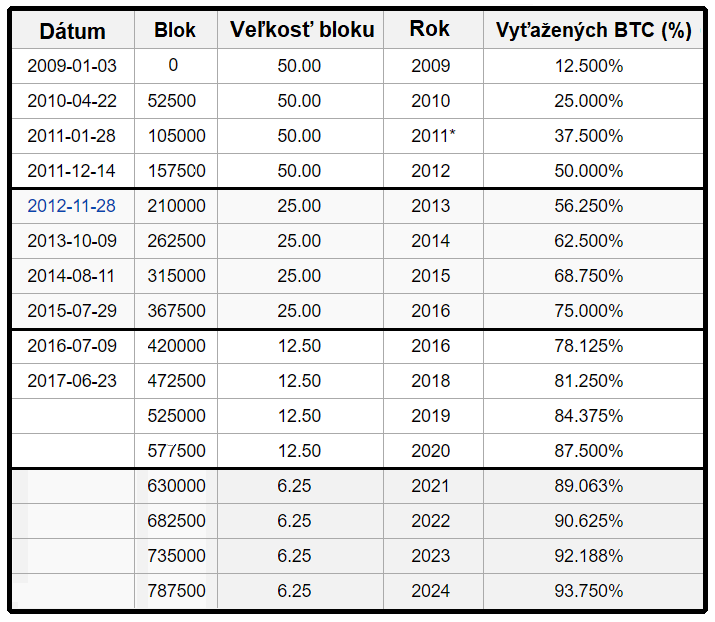
Bitcoin Block Halving – Once a 4 Years
In the case of Bitcoin, th block size is set at 50 BTCs, while the rule of block dividing applies (called Bitcoin Halving). This Halving event occurs always after 4 years (after every 210,000 mined blocks).
After this period, the size of 1 block (so also mining rewards) is automatically reduced by exactly half, which we can see in the table above.
- 2009: the size of 1 block of Bitcoin started at 50 BTC
- 2012: In 2012, it was reduced from 50 to 25 BTC coins
- 2016: After the mining of next 210,000 blocks, the size of 1 block was again reduced by half, ie from 25 to 12.5 BTC coins every 10 minutes
- And in 2020 again by half less. From 12.5 to 6.25 BTC coins and so on.
The fact is that:
First half of all Bitcoins that will ever exist in the world were mined for the first 4 years of Bitcoin’s existence (2009-2013). However, the second half will be mined for approximately another 128 years (2013-2141). Thanks to Halving.
Thus, there will be only 21 million Bitcoin coins (limited supply). However, thanks to Halving, not all BTCs have been mined so far. But by the time you read this article, most of them (91%) are already mined and only crumbs remain (approximately 9% of coins).
However, these 9% of Bitcoins will be mined gradually for the next 121 years, so every year only smaller and smaller crumbs of BTC will get into market, which is great news for miners (even bigger scarcity).
Limited supply is a strong psychological factor that causes the price of an asset … Yes, yes. It should grow!
But the number of Miners Increases thus will be Bitcoin Mined Out Sooner than 2141?
How is it possible that the last Bitcoin will be mined in 20141, when there are more and more miners (investors and machines that mine) every year?
That is why the algorithms of each cryptocurrency include an automatically changing parameter, which is the Mining Difficulty. But to understand the difficulty, firstly we have to understand hashrate.
#3 Hashrate (Mining Network Power)
The base unit of hashrate is Hash per second (H/s). There are 2 meanings of hashrate:
#1 An indicator that shows the performance of a single cryptocurrency mining machine.
#2 Network hashrate is the total (world) hashrate, so the sum of the performance of all these mining machines for a certain cryptocurrency (worldwide together).
So Network Hashrate shows us How many “people” currently mine cryptocurrency and whether this number increases or decreases. Bitcoin Mining Hashrate Chart Here.
Network Hashrate tends to Grow
Overall network hashrate is almost constantly growing. This is because of 3 Main Reasons:
- Manufacturers produce more and more powerfull miners. Today’s miners have 3 times higher performance and mining efficiency than miner for the same price from 5 years ago.
- The popularization of cryptocurrencies is growing that cause the count of miners grows
- Growing crypto prices and profits from mining (thus more miners invest in mining)
But when the count of miners almost always grows, should this theoretically means that Bitcoin will be mined sooner than in 2141?
Well, because the average time to mine 1 block is fixed at 10 minutes, the already mentioned Mining Difficulty indicator comes into play, which ensures the whole thing.
#4 Mining Difficulty
Difficulty is one of the most important factors in the cryptocurrency mining. Difficulty directly affects the final yield and profitability for the investors. Thanks to Mining Difficulty, there is maintained:
- Average time to mine 1 Block of Bitcoin (10 minutes)
- And thus also the year, when the last BTC coin will be mined (2141)
But what is Mining Difficulty and how does it works? Difficulty is an automatically changing parameter for which the rule applies:
If the total Bitcoin network hashrate grows, the Mining difficulty also grows (automatically).
In translation: The more people mine the cryptocurrency, the smaller the amount each miner gets as an reward. And this principle is invariably set directly in the algorithms of each cryptocurrency.
But does this mean that Investors Earn Less? Not really. This is because another (theoretical) principle of mining applies here.
Mining Principle #2
Why do more and more people start to mine cryptocurrencies? Because mining achieves higher and higher profits. Why? Because of the price of cryptocurrencies that grows in long-term. Cryptocurrency mining to sum up:
- The price of cryptocurrency grows
- Thus mining profits also grow
- Therefore, the number of miners grows
- And thus the mining difficulty grows also
So you mine less amounts of coins, but they have a higher value (price).
That´s how crypto mining works.
PS: Difficulty is automated, but also time-delayed indicator. After the increase of the Hashrate, the difficulty moevs after approximately 14 days (not instantly).
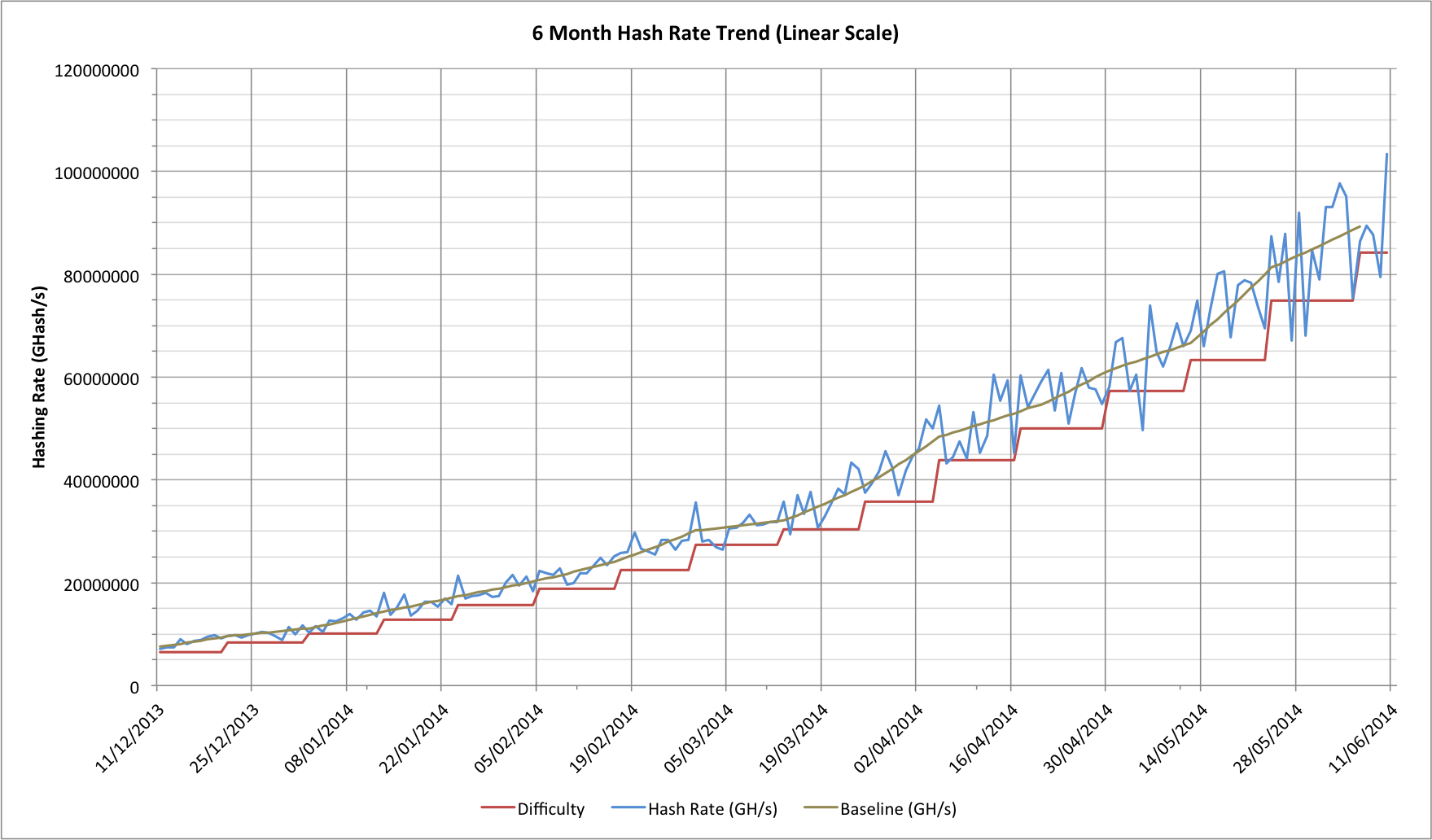
Blue Curve – Network Hashrate of the Bitcoin
Red curve – Bitcoin mining Difficulty
Graph borrowed from Coinwarz.com
How to start mining cryptocurrencies?
There are 5 Different Ways you can start making money on mining. Today.
Finally, an explanation of the “amount” in which are cryptocurrencies mined. We already know that when you mine-out coins of any cryptocurrency, in reality you mine out block of coins. But important infromation, you can mine either one whole block or none. No quarters or parts of the block.
You can mine either one whole block or none. No quarters or parts of the block.
In 2009, this was not a problem because there were few mining-investors, which means there was also low difficulty). But with today’s price of bitcoin, thousands miners are in, so difficulty of mining is quite high.
One Bitcoin block consists of 6,25 BTC with a current value of approximately 130 000 Euros. To mine that amount of BTC coins in 10 minutes, you need a really large computing power worth hundreds of thousands Euros. In translation, you need tens of Bitcoin Miners to mine whole 1 Bitcoin block todays. But of course, there is a simple solutions – Mining Pool.
Mining Pool
Above we talk about mining called solo-mining. You try to mine alone so it is quite difficult because to mine-out 1 whole block may take a few months. Until then you earned nothing. Zero. Therefore already in 2010 miners “invented” simple solution.
- Mining investors get merged into bigger group
- Hashrate of your miners is connected to thousands of other miners
- It is formed 1 large group with huge hashrate power, that already do can mine few bitcoin blocks each day (not once a several months)
- Therefore, you receive mined coins regularly every single day
- This is the thing so-called Mining Pool
By the way, the “invention” of the very first Bitcoin mining pool in the world comes from Czech Republic from Marek Palatinus (SlushPool).

Mining Pool – What is it and How does it work?
Mining pool unites thousands of miners into one unit, who contribute to it with their hashrate (miners). This creates huge clusters of mining power.
With many times more computing power, from a large number of miners, the probability of mining an entire block of Bitcoin increases rapidly. It is therefore almost certain that every day this pool will mine dozens of blocks of cryptocurrency (unlike the mentioned solo mining, when you would mine 1 block maybe once a few weeks). The principle of equivalence applies in mining pool.
The more power (number of miners) the miner (investor) puts into the pool, the greater the share of the mined block (coins) he gets. Simple.
Hashing Algorithm
As we have already mentioned, mining takes place using specialized hardware and software. However, when decrypting (verifying) transactions, your Mining computer must follow certain rules (encryption formulas). And it is the algorithm that is the key of the formulas (system) according to which the miner verifies the transaction of the given cryptocurrency.
There are approximately 60 various mining algorithms in the world. However, each is connected only to a certain type (group) of digital names.
There are approximately 60 various hashing algorithms in the world.
For example, SHA 256 algorithm is used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Bitcoin-Cash, Digibyte and other. Here is an overview of the next most common algorithms:
- SCRYPT – algorithm of Litecoin, Dogecoin, Verge and others ..
- Ethash – an algorithm of coins as Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, Expanse, Musicoin and others
- Equihash – Zcash, ZClassic, Komodo …
- CryptoNight – Monero, SumoKoin …
Here is an overview of all algorithms and a complete list of all cryptocurrencies that work on a given algorithm.
 GPU Mining Rigs – profi manufacturing since @2015
GPU Mining Rigs – profi manufacturing since @2015 How to Save on Energy up to 3500€ / 1 miner?
How to Save on Energy up to 3500€ / 1 miner? ITCA Dias Enterprise : 60 x GPU
ITCA Dias Enterprise : 60 x GPU How Mining Works?
How Mining Works?





